목적
- Hibernate setAutoCommit 최적화를 통한 성능 튜닝
배경
- 야놀자 쿠폰 API 서버 개발을 담당하고 있으며, APM Pinpoint를 통해 Transaction 전후로 setAutoCommit(false) & setAutoCommit(true) 쿼리를 반복 수행하는 것을 확인하였습니다.
- 분석 결과 각 setAutoCommit은 평균적으로 1~3ms가 소요되고 있었습니다.
- 1개의 Transaction일 경우 setAutoCommit은 2번 호출되며, 수행 시간은 2~6ms가 소요됩니다.
N개의 Nested Transaction일 경우 2N번 호출되어, 즉, 2N~6N ms가 소요됩니다.- 아래는 Nested Transaction인해 setAutoCommit이 2 * N 번 발생한 실제 케이스입니다.
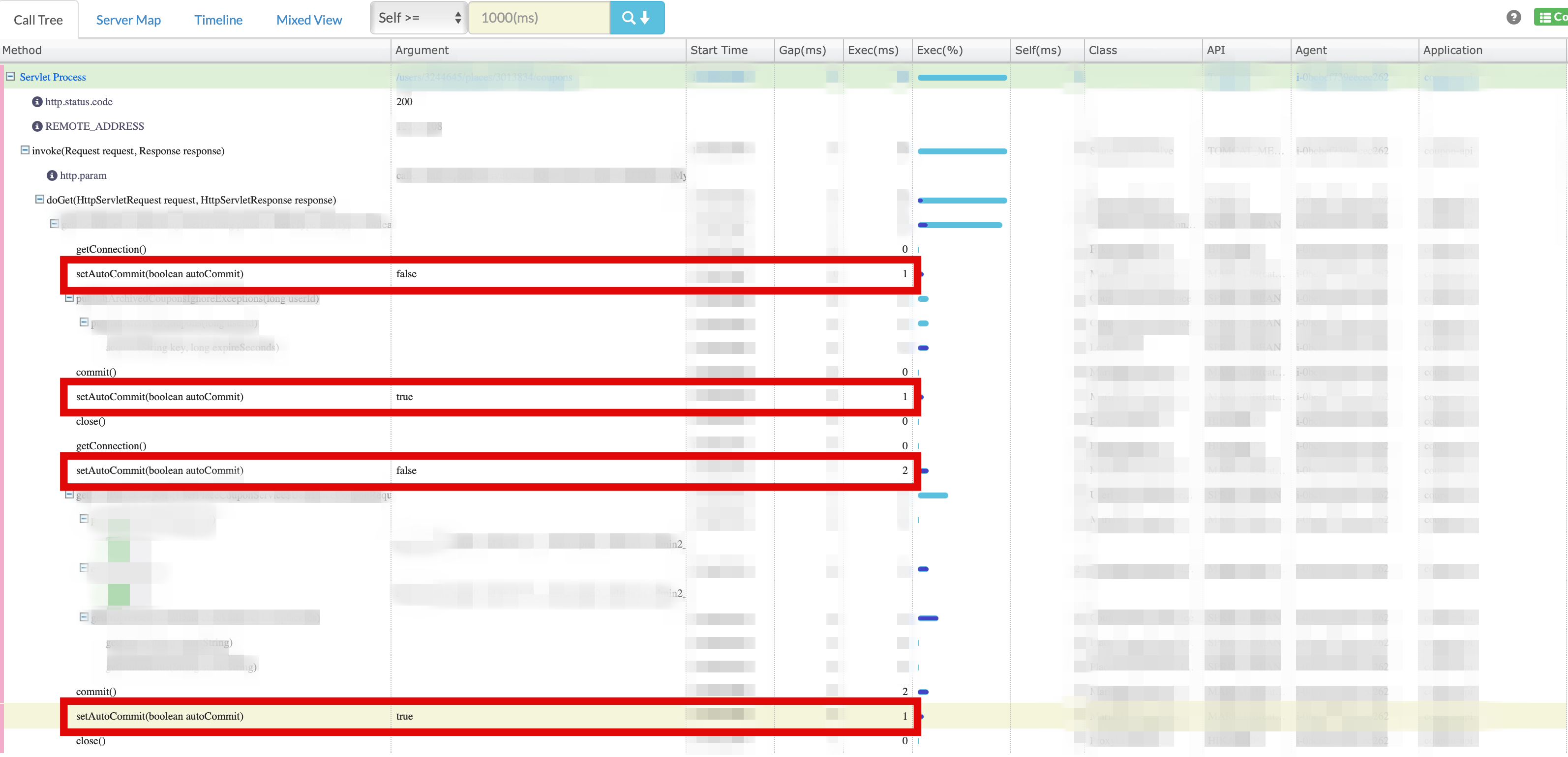
- 3개의 Nested Transaction을 예로 들면, 비지니스 수행 시간이 아닌, setAutoCommit 작업에만 6~36ms 소요될 수 있습니다.
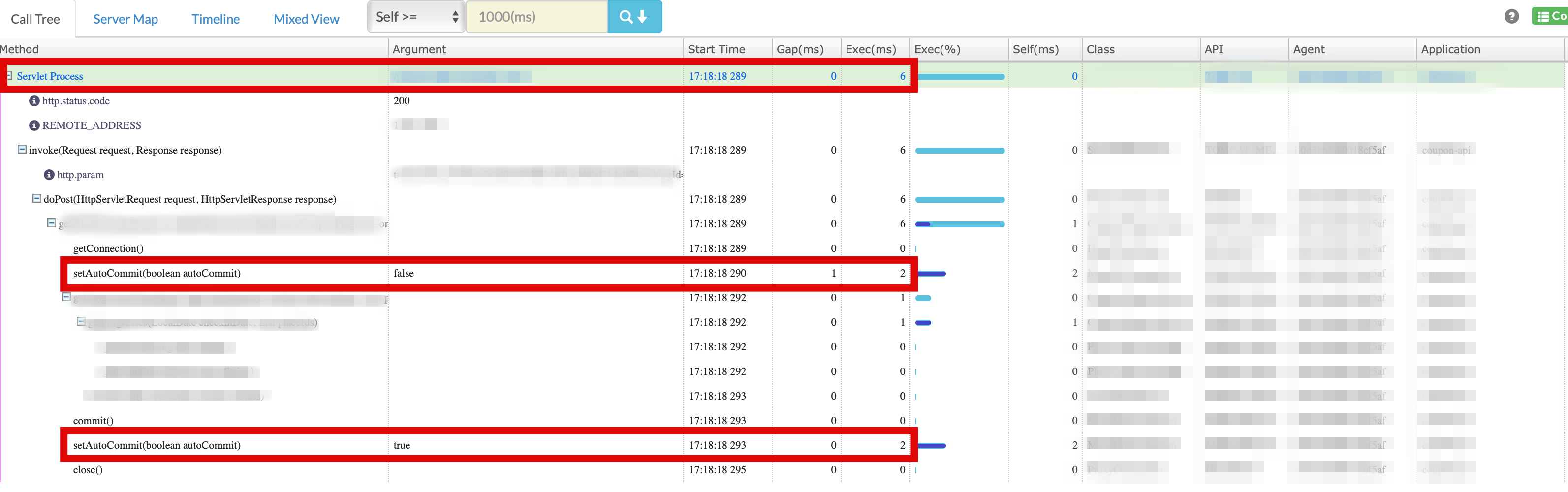
캐시를 타서 총 6ms의 응답이 걸렸는데, setAutoCommit을 수행하는데 4ms가 걸린 어이없는 경우도 있습니다.- 아래가 그 실제 케이스입니다.
- 아래의 경우에는 setAutoCommit을 최적화하면 2ms 의 응답이 가능하게 됩니다.
- setAutoCommit은
DB에 실제로 쿼리를 수행하기에 초당 수천건의 트랜잭션이 발생하면, DB에 부하를 줄 수 있고 API 응답시간도 느려지게 됩니다. - 따라서, setAutoCommit을 최적화하여 성능을 개선하고자 합니다.
환경
- JAVA 8
- Spring Boot 2.x
- Spring Data JPA 2.x
- Hibernate 5.2.x
- QueryDSL 4.2.x
- Hazelcast 3.11.x
- MariaDB 10.0.x (InnoDB-5.6.x)
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
튜닝의 핵심을 짚고 넘어가자
- Transaction 실행 및 종료시, setAutoCommit() 실행이 필요. 이는 Connection을 통해 auto commit 여부 확인이 필요.
- Hibernate의 구현상, auto commit 상태를 체크하고, Connection의 autoCommit이 true일 경우 이를 꺼야하는 구현이 존재
- 자바 챔피언 & 하이버네이트 커미터 아저씨가 쓴 문서 의 Delaying the resource-local connection acquisition 항목 참조
- DBCP session level에 setAutoCommit=false를 설정하고, Hibernate 설정(hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit)을 통한 hint로 Connection을 통한 auto commit 여부 확인을 skip
문제 분석
- AutoCommit 이란?
- 쿼리문이 수행됬을 때 TRUE 혹은 FALSE 여부 따라 변경사항을 DB에 즉시 반영 여부를 결정한다.
- Transaction으로 묶어서 작업을 수행할 경우 True로 되어 있으면 즉시 반영 된다.
- 따라서, Hibernate에서는 트랜잭션 전 후로 setAutoCommit(false) → 쿼리 1 수행 → 쿼리 2 수행 → setAutoCommit(true) → Commit 또는 Rollback 를 수행하게된다.
- 이를 통해 Transaction 작업 단위로 묶인, 작업의 일관성 및 정합성을 유지한다.
- 왜 setAutoCommit()을 자주 하면 비효율 적일까?
- 실제 DB에 쿼리를 날리게 되므로 비효율적이다.
-
현재 MariaDB 커넥터를 쓰므로 MariaDbConnection.java 구현체의 setAutoCommit() 코드를 보자.
< MariaDbConnection.java > /** * Sets whether this connection is auto commited. * * @param autoCommit if it should be auto commited. * @throws SQLException if something goes wrong talking to the server. */ public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException { if (autoCommit == getAutoCommit()) return; try (Statement stmt = createStatement()) { stateFlag |= ConnectionState.STATE_AUTOCOMMIT; stmt.executeUpdate("set autocommit=" + ((autoCommit) ? "1" : "0")); } }
- 그러면 어떻게 해야 setAutoCommit()을 하지 않을 수 있을까?
- AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java 및 구현체인 LogicalConnectionManagementImpl.java 참조
- begin() 할때 doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled를 호출하여 체크한다.
- 이때 바로 하이버네이트의 (hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit) 설정을 참조한다.
- 만약 false로 반환되면, determineInitialAutoCommitMode()를 수행하면서 안에서 getAutoCommit()을 수행하여 현재 DB 커넥션의 autoCommit 설정을 확인한다.
-
만약 true로 반환되면, 조건문의 앞단에서 실패하여 뒤에 determineInitialAutoCommitMode()를 수행하지 않으면서 getAutoCommit()을 하지 않는다.
- 그렇다면 getAutoCommit()을 하는 이유는 ?
- 트랜잭션 시작할때 초기 AutoCommit 설정을 알기 위해서 한다.
- 트랜잭션 시작할때 초기 AutoCommit 구해서 initiallyAutoCommit로 저장하고 있다가, 쿼리문 수행이 다 종료되면, 이후에 initiallyAutoCommit를 가져와서 원상복구한다.
- 즉, hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true을 하면 determineInitialAutoCommitMode()를 수행하지 않는다고 보면 된다.
-
determineInitialAutoCommitMode()는 동적으로 현재 커넥션의 설정을 확인하는 getAutoCommit()를 수행하기에 성능 향상 포인트다.
- 또한, AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java의 begin()을 보자.
- doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled()를 호출하여 false이면 setAutoCommit()을 수행하게 되고 true면 수행하지 않는다.
-
결과적으로, hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true로 놓게 되면 setAutoCommit()과 getAutoCommit()을 최소화 할 수 있다.
- hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true로 놓게 되면, hibernate가 DBCP에서 설정한 autoCommit을 믿고 쓴다는 의미로 볼 수 있다.
- false로의 설정은 믿지 못한다는 의미로, 지속적으로 getAutoCommit()을 호출해서 현재 설정을 확인해서 다르면 setAutoCommit으로 설정을 바꾼다.
-
필요 없는 상황인데 이를 반복하니 비효율적이다.
-
마지막으로,
DBCP autoCommit 설정을 true로 두게 되면 무조건 커밋이 되기에, DBCP의 autoCommit 설정은 반드시 false로 두어야 한다.< LogicalConnectionManagementImpl.java> @Override public void begin() { initiallyAutoCommit = !doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled() && determineInitialAutoCommitMode( getConnectionForTransactionManagement() ); super.begin(); } < LogicalConnectionManagementImpl.java> @Override protected void afterCompletion() { afterTransaction(); resetConnection( initiallyAutoCommit ); initiallyAutoCommit = false; } < AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java> protected static boolean determineInitialAutoCommitMode(Connection providedConnection) { try { return providedConnection.getAutoCommit(); } catch (SQLException e) { log.debug( "Unable to ascertain initial auto-commit state of provided connection; assuming auto-commit" ); return true; } } < AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java> @Override public void begin() { try { if ( !doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled() ) { log.trace( "Preparing to begin transaction via JDBC Connection.setAutoCommit(false)" ); getConnectionForTransactionManagement().setAutoCommit( false ); log.trace( "Transaction begun via JDBC Connection.setAutoCommit(false)" ); } status = TransactionStatus.ACTIVE; } catch( SQLException e ) { throw new TransactionException( "JDBC begin transaction failed: ", e ); } }
- AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java 및 구현체인 LogicalConnectionManagementImpl.java 참조
- 부가적으로 얻을 수 있는 성능 향상 효과
- hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true 설정으로 인해 얻을 수 있는 추가 효과
- 기존에 동적으로 현재 커넥션의 autoCommit 설정을 확인하기 위해 determineInitialAutoCommitMode() 를 수행한다.
- 이때,
getConnectionForTransactionManagement() 를 통해 실제 DB 커넥션을 가져오게 되는데 이를 나중으로 미루어 Throughput을 향상시킬 수 있다.- doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled()을 통해 hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit 설정을 체크한다.
- doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled()가 false일 경우 determineInitialAutoCommitMode()를 수행하며 setAutoCommit을 수행한다.
- 이때, getConnectionForTransactionManagement()을 수행하는데 setAutoCommit을 하려고 여기서 실제 DB 커넥션을 가져온다.
-
따라서, hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit을 true로 설정할 경우, 커넥션을 가져오는 것을 미룰 수 있어 Throughput을 향상 시킬 수 있다.
< LogicalConnectionManagementImpl.java> @Override public void begin() { initiallyAutoCommit = !doConnectionsFromProviderHaveAutoCommitDisabled() && determineInitialAutoCommitMode( getConnectionForTransactionManagement() ); super.begin(); } < AbstractLogicalConnectionImplementor.java> protected static boolean determineInitialAutoCommitMode(Connection providedConnection) { try { return providedConnection.getAutoCommit(); } catch (SQLException e) { log.debug( "Unable to ascertain initial auto-commit state of provided connection; assuming auto-commit" ); return true; } }-
- 커넥션 가져오기를 미루고 난 후, 나중에 PreparedStatement 관련 수행시 connection()을 통해 실제 물리 커넥션을 가져오는 코드
-
PreparedStatement 수행 때로 DB 커넥션을 가져오는 시간을 미루어 Throughput을 향상 시킬 수 있다.
< StatementPreparerImpl.java > @Override public PreparedStatement prepareQueryStatement( String sql, final boolean isCallable, final ScrollMode scrollMode) { if ( scrollMode != null && !scrollMode.equals( ScrollMode.FORWARD_ONLY ) ) { if ( ! settings().isScrollableResultSetsEnabled() ) { throw new AssertionFailure("scrollable result sets are not enabled"); } final PreparedStatement ps = new QueryStatementPreparationTemplate( sql ) { public PreparedStatement doPrepare() throws SQLException { return isCallable ? connection().prepareCall( sql, scrollMode.toResultSetType(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY ) : connection().prepareStatement( sql, scrollMode.toResultSetType(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY ); } }.prepareStatement(); jdbcCoordinator.registerLastQuery( ps ); return ps; } else { final PreparedStatement ps = new QueryStatementPreparationTemplate( sql ) { public PreparedStatement doPrepare() throws SQLException { return isCallable ? connection().prepareCall( sql ) : connection().prepareStatement( sql ); } }.prepareStatement(); jdbcCoordinator.registerLastQuery( ps ); return ps; } } - -
-
- DB 커넥션은 어떻게 가져오는가 ?
- 커넥션을 가져오는 요청을 하게되면 LogicalConnectionManagedImpl.java 구현체를 실행한다.
- jdbcConnectionAccess.obtainConnection()을 하게 되면 실제 커넥션을 가져온다.
- 내부적으로 NonContextualJdbcConnectionAccess.java을 참조하고 있으며 obtainConnection() 호출시 connectionProvider를 통해 커넥션을 가져온다.
-
현재 커넥션 프로바이더가 HikariCP이기 때문에, HikariCP의 커넥션 풀에서 가져온다.
private Connection acquireConnectionIfNeeded() { if ( physicalConnection == null ) { // todo : is this the right place for these observer calls? observer.jdbcConnectionAcquisitionStart(); try { physicalConnection = jdbcConnectionAccess.obtainConnection(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw sqlExceptionHelper.convert( e, "Unable to acquire JDBC Connection" ); } finally { observer.jdbcConnectionAcquisitionEnd( physicalConnection ); } } return physicalConnection; } - - -
-
위에서 jdbcConnectionAccess.obtainConnection()을 하게 되면 아래 소스를 참조한다.
< NonContextualJdbcConnectionAccess.java > @Override public Connection obtainConnection() throws SQLException { try { listener.jdbcConnectionAcquisitionStart(); return connectionProvider.getConnection(); } finally { listener.jdbcConnectionAcquisitionEnd(); } }
-
- 커넥션을 가져오는 요청을 하게되면 LogicalConnectionManagedImpl.java 구현체를 실행한다.
-
- 현재 connectionProvider를 HikariCP를 쓰고 있기에, 위에서 connectionProvider.getConnection()를 호출하면 아래의 소스를 참조한다.
- 커넥션을 어떻게 가져오는지 살펴보자.
-
만약, Hikari의 커넥션풀이 null이면 새로 생성하고, null아니면 하나 가져온다.
< HikariDataSource.java > 의 getConnection() 구현체 @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { if (isClosed()) { throw new SQLException("HikariDataSource " + this + " has been closed."); } if (fastPathPool != null) { return fastPathPool.getConnection(); } // See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-checked_locking#Usage_in_Java HikariPool result = pool; if (result == null) { synchronized (this) { result = pool; if (result == null) { validate(); LOGGER.info("{} - Starting...", getPoolName()); try { pool = result = new HikariPool(this); this.seal(); } catch (PoolInitializationException pie) { if (pie.getCause() instanceof SQLException) { throw (SQLException) pie.getCause(); } else { throw pie; } } LOGGER.info("{} - Start completed.", getPoolName()); } } } return result.getConnection(); }
- 현재 connectionProvider를 HikariCP를 쓰고 있기에, 위에서 connectionProvider.getConnection()를 호출하면 아래의 소스를 참조한다.
분석 결론
- hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit 설정은 DBCP 설정의 autoCommit을 믿고 사용하는 설정이다.
- 즉, DBCP의 autoCommit 설정이 매우 중요하다.
- 만약 hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true로 놓고 DBCP의 autoCommit을 true로 놓게되면?
- DBCP가 커넥션을 생성하여 가지고 있으므로, 생성 시점부터 항상 autoCommit=true라 트랜잭션 안에 메소드가 수행하다 실패해도 롤백이 안된다.
- 따라서,
hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit=true를 사용할거면 DBCP의 autoCommit을 false로 놓아서 트랜잭션 단위로 동작할 수 있도록 해야한다. - 필수 참고 문서
적용 방법
- 적용 후에는 반드시, Transaction Rollback & Commit 정상 작동을 확인해야 합니다.
- yml 기준 설정
- DBCP의 auto-commit: false
-
hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit: true
spring: datasource: hikari: auto-commit: false jpa: properties: hibernate.connection.provider_disables_autocommit: true
적용 결과
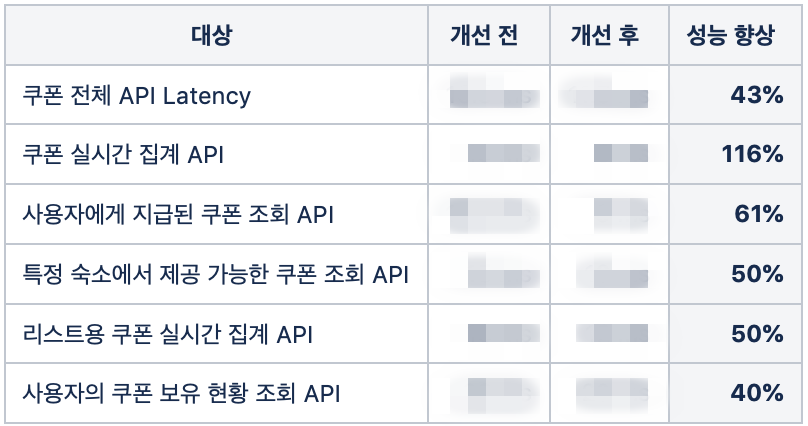
- 결과 요약
- setAutoCommit 최적화로
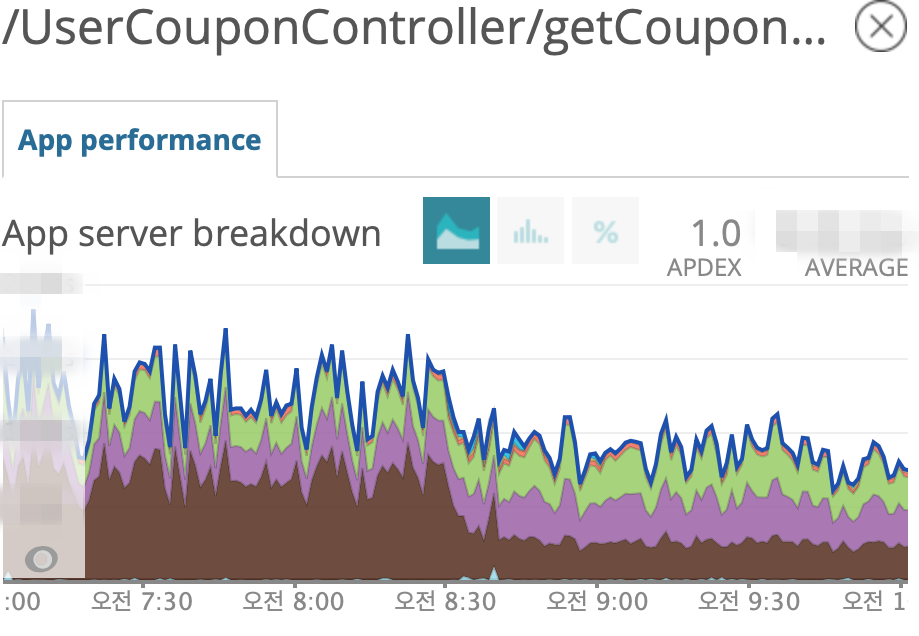
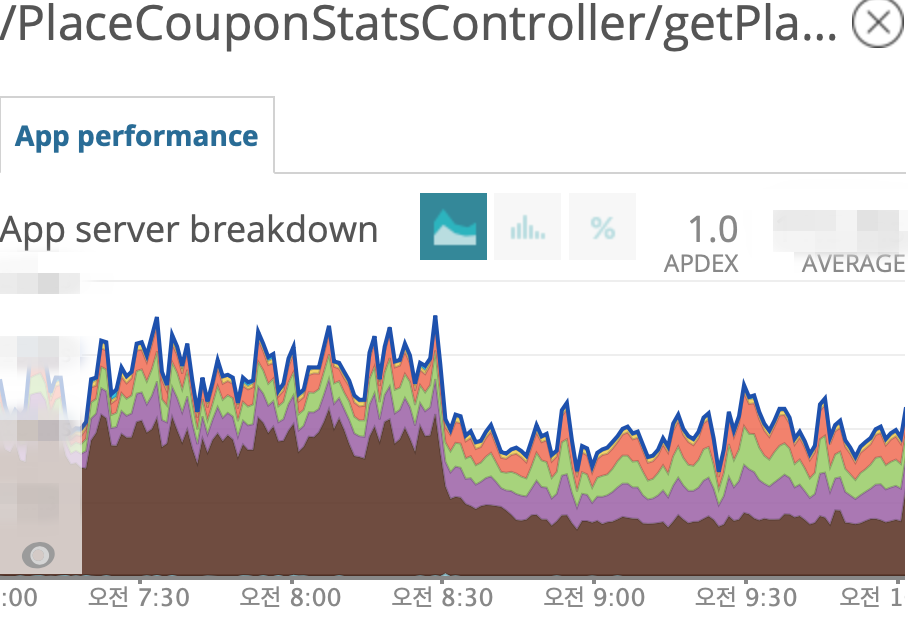
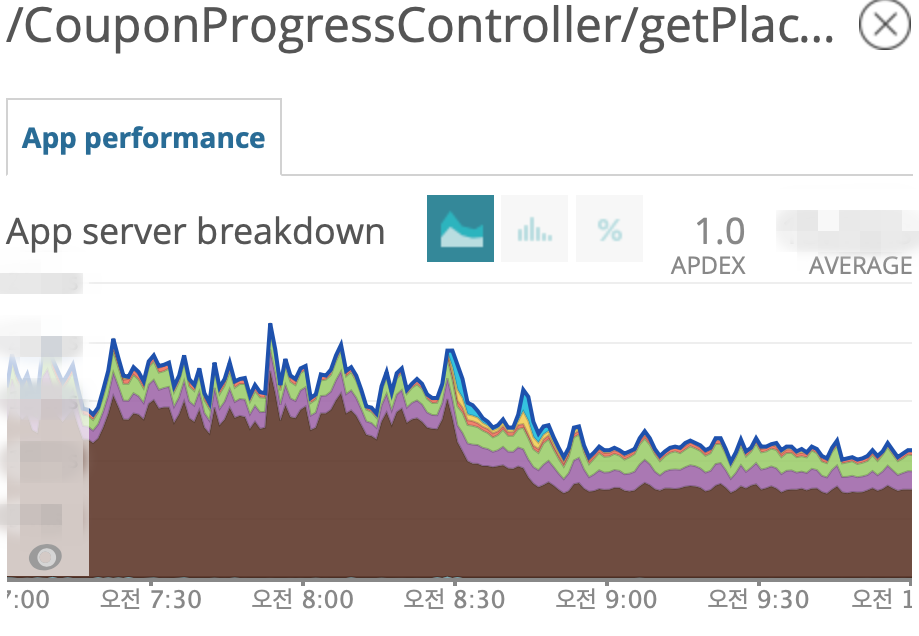
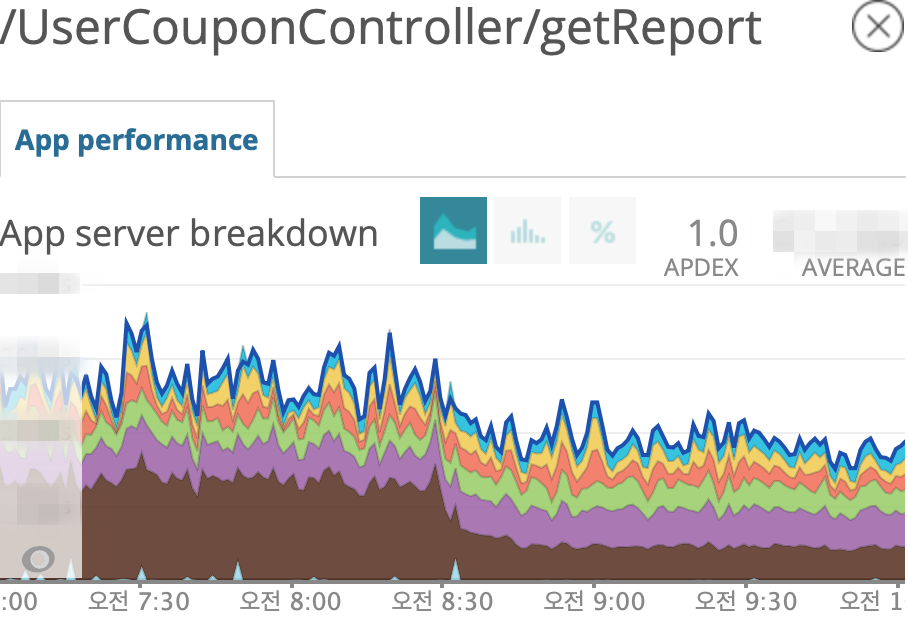
쿠폰 전체 API에 대해 평균적으로 43%의 성능 향상
- setAutoCommit 최적화로
- API 별 분석
- 결과 이미지
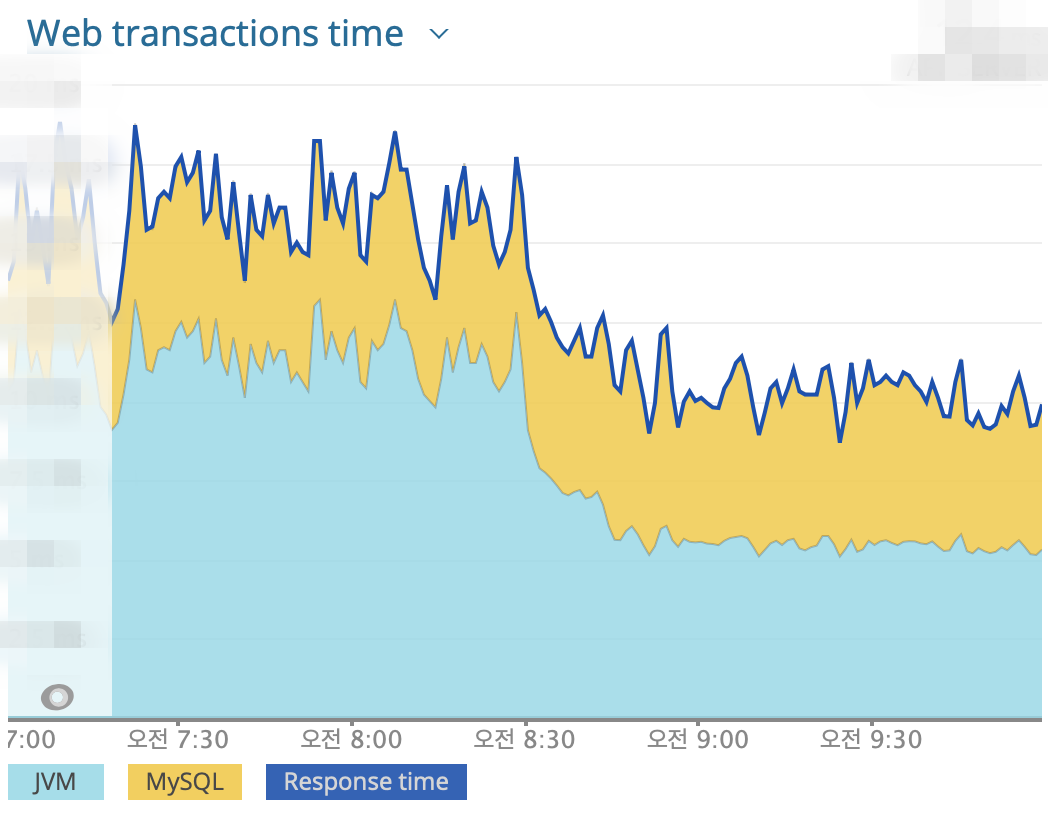
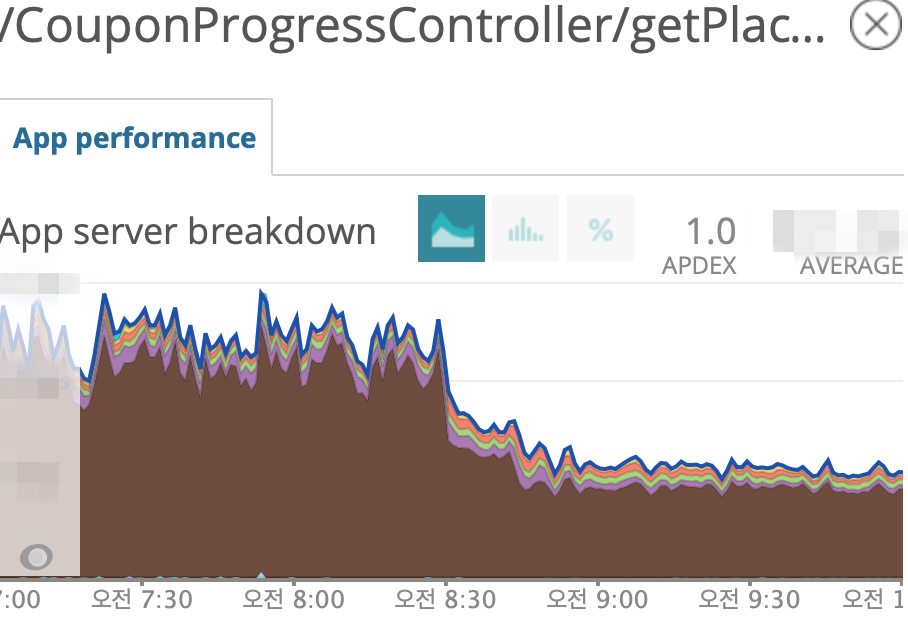
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 쿠폰 전체 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 쿠폰 실시간 집계 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 사용자에게 지급된 쿠폰 조회 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 특정 숙소에서 제공 가능한 쿠폰 조회 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 리스트용 쿠폰 실시간 집계 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 사용자의 쿠폰 보유 현황 조회 API Latency 변화
- setAutoCommit 최적화 전 후 쿠폰 전체 API Latency 변화
마치며
- Hibernate에서는 너무 많은 것들을 지원해주기에, 생각보다 최적화 되지 않은 부분들이 많다.
- 당연하게도, 사용 빈도가 높은 작업일 경우 튜닝의 효과가 매우 크다.
- JDBC Driver 설정 튜닝이라던지.. 개선 전후의 TPS가 천단위로 차이가 날 때도 많다…
- 결론은, 하나의 설정을 적용하더라도 내부 구현체를 열어보고 반드시 동작 방식을 분석하고 사용해야 할 것이다.
 pkgonan
pkgonan